BENEFITS OF GANODERMA
Our Magic Ingredient – Ganoderma lucidum
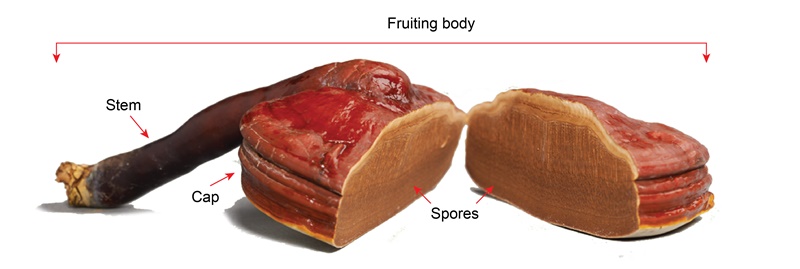
Ganoderma lucidum has three main parts: the mycelium, fruiting body and spores. The mycelium is the white villiform at the base of the mushroom that supplies needed nutrients for its growth, while the fruiting body is the ‘umbrella’ part of the mushroom, and the spores are its seeds. All parts of Ganoderma, including the mycelium, fruiting body and spores, are edible and have various medicinal properties that can prevent and ameliorate human diseases.
Ganoderma as an Overall Health Booster
Ganoderma lucidum is one of the best known and most researched immunomodulatory herbs. It is used to treat cases of poor immunity, as seen in individuals who experience frequent bacterial and viral infections such as the flu (influenza) due to low immune resilience.
Many studies have shown that Ganoderma lucidum extracts (including from the mycelium, fruiting bodies and spores) have the effect of enhancing the body’s natural resistance and physical well-being, resulting in optimum health.
In addition, Ganoderma lucidum is an antioxidant that protects the body from the harmful effects of free radicals. It contains Reishi polysaccharide, which combats bacteria and viruses, thus helping to boost the immune system.
Ganoderma lucidum VS Diabetes Mellitus & Its Complications
Ganoderma lucidum has been proved to have a hypoglycemic effect.
1. Stimulating blood glucose uptake
Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides (Gl-PS) have an antihyperglycemic effect by stimulating insulin secretion, enhancing blood glucose uptake by the body, which results in decreased blood glucose levels.
2. Protecting against renal injury by increasing activities of antioxidants
Many studies have demonstrated that Ganoderma lucidum extracts could improve antioxidant enzyme activities such superoxide dismutase and enhance the free-radical scavenging capacity of the body. This reduces oxidative damage to the kidney, thus protecting the kidney and preventing diabetic renal complications.
Reference:
1. Arch Pharm Res. 2012 Oct;35(10):1793-801.
Hypoglycemic effects of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides in type 2 diabetic mice.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23139131
2. Food Chem Toxicol. 2014 Jan;63:111-8.
A novel proteoglycan from Ganoderma lucidum fruiting bodies protects kidney function and ameliorates diabetic nephropathy via its antioxidant activity in C57BL/6 db/db mice
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0278691513007217
Ganoderma lucidum VS Cardiovascular Diseases
Ganoderma lucidum has been proved to be beneficial to the health of the cardiovascular system.
1. Anti-hypercholesterolemia, preventing arteriosclerosis
Ganoderma lucidum has been proved to effectively reduce the level of total cholesterol, bad cholesterol (LDL) and triglycerides, as well as increase good cholesterol (HDL) levels. It helps to prevent the formation of atherosclerosis.
Furthermore, Ganoderma triterpenoids could inhibit the formation and biosynthesis of cholesterols in the liver, thus preventing the liver from producing an excess of cholesterol.
2. Anti-platelet & vasodilator effects
Ganoderma lucidum extracts (adenosine) are able to inhibit platelet aggregation, reducing blood viscosity and thus preventing blood vessel blockage and clot formation. They regularise blood flow in blood vessels, especially in the microcirculation, thus helping to prevent heart attacks and other cardiovascular diseases. Besides that, ganoderma adenosine works as a good vasodilator (medications that dilate blood vessels) and improves supply of blood and oxygen to various organs.
3. Anti-hypertension
Ganoderma lucidum has been shown to lower blood pressure levels through the inhibition of anti-angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) activity.
Reference:
1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005 Jul;71(7):3653-8
Effect of 26-oxygenosterols from Ganoderma lucidum and their activity as cholesterol synthesis inhibitors.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1168986/
2. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 1985 Jul;33(7):3012-5.
Isolation of an inhibitor of platelet aggregation from a fungus, Ganoderma lucidum.
https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/cpb1958/33/7/33_7_3012/_pdf
3. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2013 Oct 4;13:256.
Anti-angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) proteins from mycelia of Ganoderma lucidum (Curtis) P. Karst.
http://bmccomplementalternmed.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1472-6882-13-256
Ganoderma lucidum VS Cancers & Autoimmune Diseases
Ganoderma lucidum is known to have anti-cancer properties, derived from its chemical constituents, namely the triterpenes and polysaccharides. Triterpenes are primarily taken from the spores and have shown remarkable pharmacological and therapeutic activities on multiple human diseases, especially cancer. Triterpenes are able to reduce the rate of proliferation, induce apoptosis in human cancer cells and reduce metastatic potential. They also help to suppress inflammatory cytokine secretion in macrophage cells and reduce cancer-inducing oxidative damage by directly scavenging from radicals generated in the cell.
Polysaccharides extracted from different parts of Ganoderma lucidum induce different immune responses with varying immune potencies. Polysaccharides exert their anti-cancer effect by enhancing the host’s immune system. It also possesses anti-angiogene activity and inhibits the production of nitric oxide, an inducing agent of angiogenesis overexpressed in tumours.
Besides the capacity to fight off cancers, Ganoderma lucidum demonstrates the suppression of autoimmune diseases due to its immunomodulating effect. Autoimmune diseases are caused by immune system overactivity, in which the body attacks and damages its own tissues. Common autoimmune diseases include rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), psoriasis, type 1 diabetes and multiple sclerosis. Polysaccharides in Ganoderma lucidum inhibit overactive immune responses and reduces inflammation caused by them.








